Boost Your Health Insurance IQ
Go from confused to confident with these health insurance basics.

What Is Health Insurance?
Health insurance is different across the world, but here in the United States, it is designed to help you cover the costs of medical care for yourself and/or for your family. Whether you use it or not, you pay a monthly premium for your insurance. If you need medical care, health insurance covers some of those costs. What they cover depends on the type of plan you have and what type of doctor you see.
Good to Know: Health Insurance Terms
Sometimes health insurance terms can feel like a different language. We've broken down these terms to make them easy to understand. These terms apply to your policy year, typically a 12-month period when you have coverage through your health plan.
Access-Related Insurance Terms
These terms are associated with how to access medical care for your particular health plan. Depending on your plan, you may have different requirements associated with accessing care.
Cost-Related Insurance Terms
These terms are associated with the care that you receive. You'll typically see them on your Explanation of Benefits (EOB) after seeking services and your plan's summary of benefits. Depending on your plan, these costs can vary.
How to Read Your Explanation of Benefits (EOB)
Your EOB is a summary of your insurance coverage for a billed service, it is NOT a bill.
Different Types of Health Insurance
There are three main types of health insurance plans. All have their unique characteristics. Being familiar with the types of plans available can help you either choose the plan that fits your needs best or understand your plan better.
HMO
- Typically can only use in-network providers, it does not include out-of-network coverage.
- Referrals are required for most services.
- Deductibles and out-of-pocket costs will depend on the specific plan
- May require selecting a primary care provider as part of the plan.
PPO
- Typically has in-network and out-of-network coverage options.
- Most do not require referrals for additional services.
- Deductibles and out-of-pocket costs will depend on the specific plan
High-Deductible Health Plan
- Operates similarly to a PPO
- The monthly premium is generally lower than a PPO plan
- Deductibles are set higher but often include a Health Savings Account (HSA)
How You and Your Insurer Share Costs
Most health plans have a policy year starting January 1st and ending December 31st, with some exceptions. Here are some helpful ways to see how medical costs are covered between you and your health care plan. The patient's responsibility (how much you would owe) depends on your plan type, deductibles, and your out-of-pocket maximum.
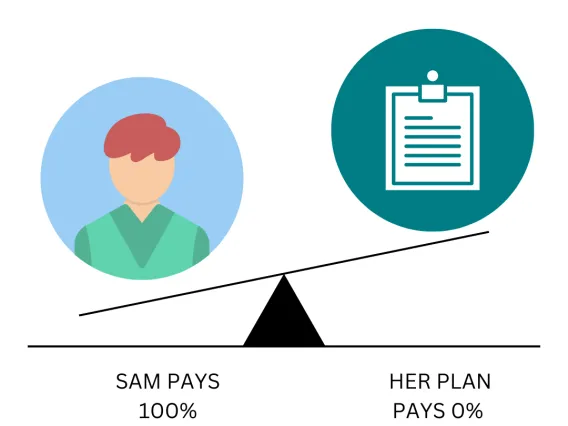
Sam's Plan Deductible: $1,500
Sam hasn’t reached her $1,500 deductible yet
Her plan doesn’t pay any of the costs.
Office visit costs: $125
Sam pays: $125
Her plan pays: $0
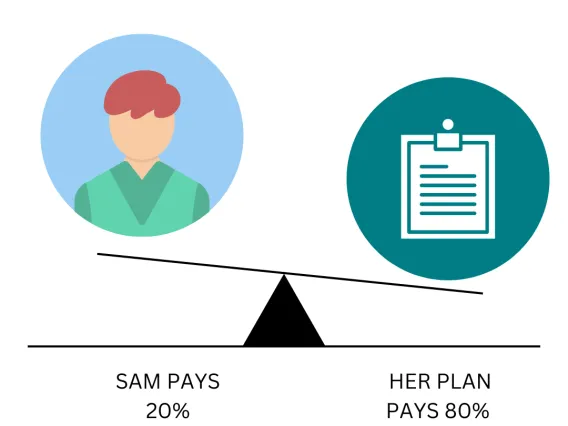
Coinsurance: 20%
Sam reaches her $1,500 deductible, coinsurance begins
Sam has seen a doctor several times and paid $1,500 in total, reaching her deductible. So her plan pays some of the costs for her next visit.
Office visit costs: $125
Sam pays: 20% of $125 = $25
Her plan pays: 80% of $125 = $100
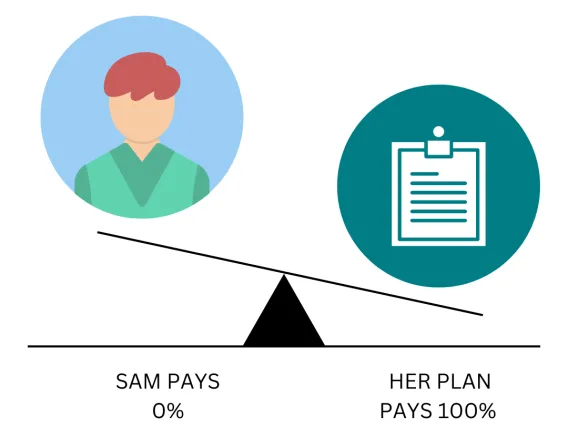
Out-of-Pocket Limit: $5,000
Sam reaches their $5,000 out-of-pocket limit
Sam has seen the doctor often and paid $5,000 in total. Her plan pays the full cost of her covered healthcare services for the rest of the year.
Office visit costs: $125
Sam pays: $0
Her plan pays: $125
(images adapted from healthcare.gov)
